Respiratory Infections and COVID-19: How Blood Thinners Interact with COVID Treatments
 Feb, 7 2026
Feb, 7 2026
Blood Thinner & COVID Treatment Interaction Checker
Interaction Result
Note: Always consult with your doctor or pharmacist before making any changes to your medication regimen.
When you're fighting a respiratory infection like COVID-19, your body isn't just battling a virus-it's also triggering dangerous changes in your blood. For people taking blood thinners, this creates a high-stakes balancing act. Too much anticoagulation and you risk bleeding. Too little, and you could develop deadly clots. The interaction between common COVID-19 treatments and anticoagulants isn't theoretical-it's happening in hospitals and pharmacies every day.
Why COVID-19 Makes Blood Thinner Management So Tricky
COVID-19 doesn't just cause coughs and fevers. In severe cases, it turns your blood into a ticking time bomb. Studies show that up to 70% of critically ill patients develop tiny clots in their lung vessels, a condition called microthrombosis. This isn't random-it's a direct result of the body's inflammatory response. The virus triggers a surge in proteins like D-dimer and fibrinogen, pushing the blood into a hypercoagulable state. That means your body is primed to form clots, even in places they shouldn't.
Doctors responded quickly. The American Society of Hematology found that therapeutic-dose anticoagulants-full treatment doses, not just prevention doses-reduced death rates in hospitalized patients. But here's the catch: many of those same patients were also getting antiviral drugs like Paxlovid. And that's where things go sideways.
Paxlovid and DOACs: A Dangerous Mix
Paxlovid, the antiviral combo of nirmatrelvir and ritonavir, became a go-to treatment for high-risk patients early in the pandemic. But ritonavir? It's a powerful enzyme blocker. Specifically, it shuts down CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein-two key pathways your body uses to clear drugs like apixaban, rivaroxaban, dabigatran, and edoxaban.
When these pathways are blocked, your blood thinner doesn't get broken down. It builds up. A 2022 study in PMC9284020 showed that patients who kept taking DOACs while on Paxlovid had blood levels that spiked over 100% higher than normal. That's not a little increase-it's enough to cause major bleeding. One Reddit user described a patient who ended up in the ER with gastrointestinal bleeding after continuing full-dose rivaroxaban during Paxlovid treatment. They needed two units of blood.
But it's not just about too much drug. Dexamethasone, a steroid used to calm inflammation in severe COVID-19, does the opposite. It speeds up how fast your liver clears DOACs. Research from Testa et al. found this can cut anticoagulant levels by up to 50%. Suddenly, your blood thinner isn't working at all-and clots can form.
Warfarin Isn't Safer-It's Just Different
Many assume warfarin is easier to manage because it's been around for decades. But it's not. Warfarin's effect is measured by INR, and that number swings wildly with other drugs. Azvudine, lopinavir/ritonavir, and even dexamethasone can all push INR up or down. A 2023 case study documented a 70-year-old man whose INR jumped from 2.5 to 3.2 after adding azvudine and dexamethasone to his regimen. That’s still in the therapeutic range-but it’s a sign of how unstable things can get.
Unlike DOACs, warfarin doesn’t have a reliable way to check its level in real time. INR tests take time, and during the pandemic, many clinics reduced in-person visits. A US Pharmacist report found that time spent in the safe INR range dropped by 18-22% during the peak of the pandemic. That’s not just inconvenient-it’s dangerous.
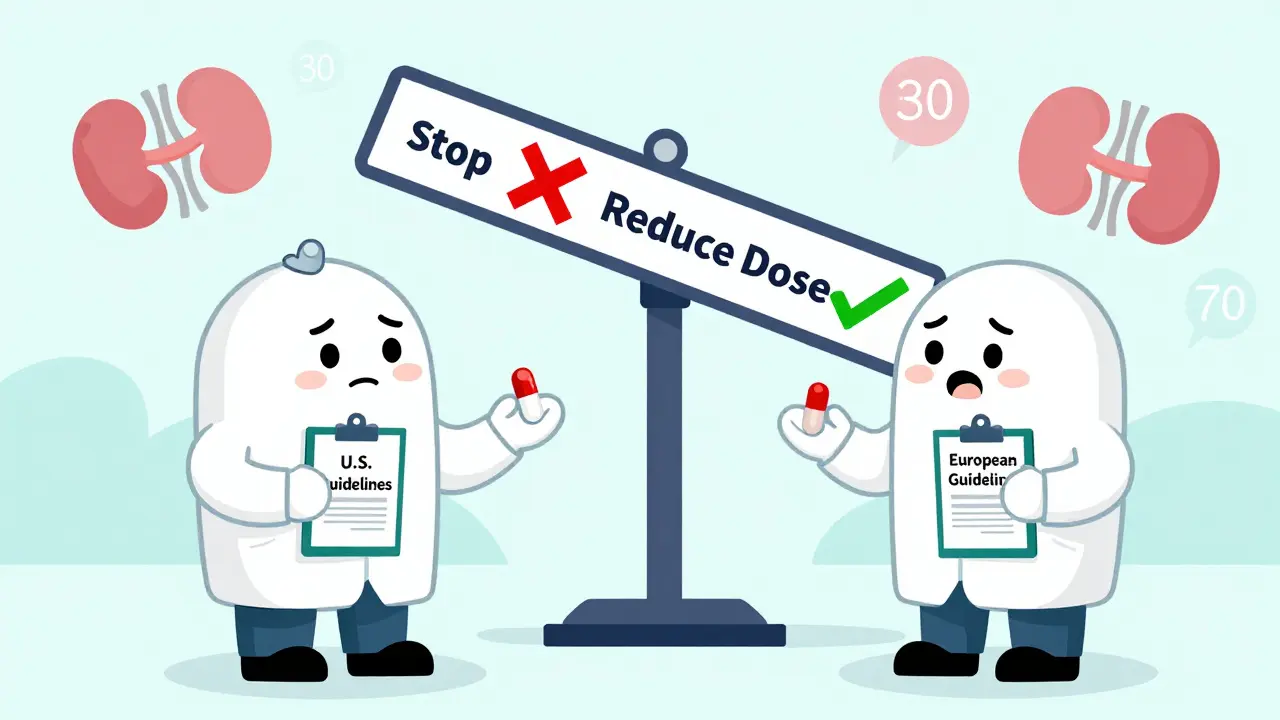
Regional Guidelines Clash-And Patients Pay the Price
Here’s where it gets messy. The U.S. and Europe don’t agree on how to handle DOACs during Paxlovid treatment.
In the U.S., the FDA and American College of Cardiology recommend avoiding DOACs entirely during Paxlovid. For rivaroxaban and apixaban, you stop the drug for the full 5-day course and restart 2 days after. For dabigatran, if your kidney function is normal (CrCl ≥50 mL/min), you can reduce the dose to 75 mg twice daily and space it out from Paxlovid by at least 12 hours.
Europe’s EMA says something different. They allow a 50% dose reduction of rivaroxaban with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. For dabigatran, they say it’s okay if kidney function is above 30 mL/min, as long as you're monitored closely.
That’s a problem for travelers, expats, or anyone with healthcare records from multiple countries. A patient might be told one thing by their U.S. doctor and another by their European pharmacist. And with 25% of elderly anticoagulated patients having kidney function between 30-50 mL/min-right in the gray zone-there’s no clear answer.
What Works in Real Life
Real-world solutions are practical, not perfect. The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists (ASHP) laid out a clear roadmap:
- For apixaban or rivaroxaban: Hold the drug for the full 5 days of Paxlovid. Restart 2 days after the last dose.
- For dabigatran: If kidney function is ≥50 mL/min, reduce dose to 75 mg twice daily and take it at least 12 hours apart from Paxlovid.
- For high-risk patients: Consider bridging with enoxaparin (a low-molecular-weight heparin) during the 5-day gap. One case shared by Dr. Sam Goldhaber showed this worked without complications.
Monitoring is non-negotiable. Anti-Xa levels should be checked daily for DOACs. For warfarin, INR should be checked at least every other day during treatment. If you're not getting tested, you're guessing-and guessing with anticoagulants can kill.
Why This Matters Beyond the Pandemic
This isn’t just a COVID-19 problem. It’s a warning shot for how we manage medications in the future. The same enzyme-blocking mechanism that makes Paxlovid effective against the virus is what makes it dangerous with blood thinners. And as more antivirals hit the market, the same issue will pop up again.
The FDA has already logged 147 cases of major bleeding linked to DOAC-Paxlovid use between January 2022 and June 2023. The Institute for Clinical and Economic Review predicts the U.S. will spend $1.2 billion annually on managing these interactions by 2025. That’s not just a healthcare cost-it’s a human cost. Emergency room visits for anticoagulation issues jumped 37% in the first pandemic year, with nearly a third directly tied to drug interactions.
What You Need to Do Now
If you're on a blood thinner and get diagnosed with COVID-19:
- Don’t stop your anticoagulant on your own. Talk to your doctor or pharmacist before making any change.
- Tell them every medication you’re taking. This includes supplements, OTC painkillers, and herbal remedies.
- Use trusted tools. The Liverpool COVID-19 Drug Interactions website updates daily and has handled over 1.2 million queries since 2020. It’s free, reliable, and used by hospitals worldwide.
- Know your kidney function. CrCl matters more than you think. If you don’t know yours, ask for a recent blood test.
- Expect more monitoring. More blood tests, more calls from your pharmacy, more follow-ups. This isn’t overreaction-it’s necessary.
The good news? Researchers are working on solutions. Pfizer’s next-generation antiviral, PF-07817883, is in Phase 2 trials and shows minimal enzyme interference. Machine learning models, like one published in Nature Medicine in 2023, can now predict interaction severity with 89.4% accuracy. And 87% of hematology experts believe these issues will be largely solved within 3-5 years.
But until then, the key is awareness, communication, and vigilance. Your blood thinner isn’t just a pill-it’s part of a complex system. And during a respiratory infection, that system is under siege. Don’t let silence be your risk.
Marie Fontaine
February 8, 2026 AT 09:24Ryan Vargas
February 8, 2026 AT 12:54Simon Critchley
February 9, 2026 AT 18:06Jessica Klaar
February 10, 2026 AT 15:55glenn mendoza
February 11, 2026 AT 13:07Jonah Mann
February 13, 2026 AT 09:48Tricia O'Sullivan
February 14, 2026 AT 17:06Brandon Osborne
February 16, 2026 AT 08:46